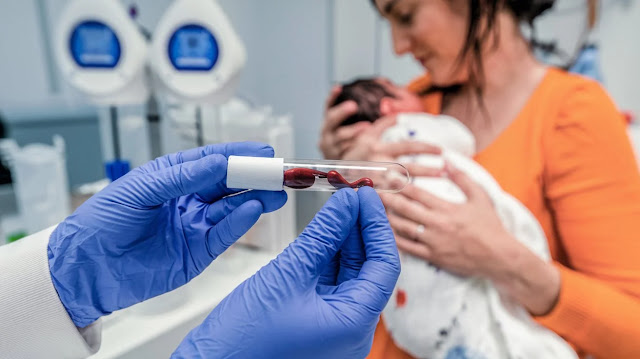
The Lifesaving Benefits of Cord Blood Banking
In recent years, cord blood banking has emerged as a revolutionary medical practice that offers immense potential for saving lives. Cord blood, which is the blood collected from the umbilical cord and placenta after childbirth, contains a rich source of stem cells that have unique regenerative capabilities. These stem cells can be used in a variety of medical treatments, including those for blood disorders, cancers, and immune deficiencies. As more research highlights the extraordinary applications of cord blood, its value continues to grow, making cord blood banking an essential consideration for expecting parents. This article delves into the lifesaving benefits of cord blood banking, its applications in modern medicine, and its potential for the future.
1. Understanding Cord Blood and Stem Cells
Cord blood is the blood that remains in the umbilical cord and placenta after the birth of a baby. It is a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), which are responsible for forming all types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These stem cells have a remarkable ability to regenerate and replace damaged or diseased cells in the body, making them highly valuable in treating a range of medical conditions.
Stem cells from cord blood are different from the controversial embryonic stem cells. They are obtained ethically, without any harm to the mother or baby, and can be stored for future use in treatments. These cells are particularly valuable because they have not been exposed to environmental factors or diseases, making them less likely to cause complications when used in therapies.
2. The Medical Applications of Cord Blood
Cord blood banking holds tremendous potential in the field of regenerative medicine. The most common use of cord blood stem cells is in the treatment of blood-related diseases such as leukemia, lymphoma, and sickle cell anemia. To date, cord blood transplants have been used to treat over 80 different diseases. This includes various types of cancers, genetic disorders, and immune system deficiencies.
2.1. Blood Disorders and Cancers
One of the primary uses of cord blood stem cells is in treating cancers like leukemia and lymphoma. Traditional cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation often destroy not only the cancer cells but also the patient’s healthy cells. Cord blood stem cell transplants can help restore the patient’s bone marrow and immune system, giving them a new lease on life.
Additionally, cord blood stem cells have been used to treat conditions such as sickle cell anemia and thalassemia. These are genetic blood disorders where abnormal hemoglobin production affects the red blood cells. A successful stem cell transplant can help patients produce normal red blood cells, significantly improving their quality of life.
2.2. Immune System Deficiencies
Cord blood stem cells can also be used to treat inherited immune system disorders, such as severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also known as “bubble boy disease.” SCID is a rare genetic disorder where the immune system is severely compromised, leaving patients vulnerable to infections. A cord blood transplant can replace the defective immune system with healthy stem cells, helping the patient lead a normal, infection-free life.
2.3. Metabolic and Genetic Disorders
Beyond blood disorders and immune deficiencies, cord blood stem cells have been used to treat metabolic disorders such as Hurler syndrome and adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD). These conditions result from enzyme deficiencies that affect the body’s ability to break down certain substances, leading to severe developmental issues and even early death. Cord blood stem cell transplants can provide the missing enzymes or replace the damaged cells, giving patients a chance at a longer, healthier life.
3. Advantages of Cord Blood Over Other Stem Cell Sources
Cord blood offers several advantages over other stem cell sources, such as bone marrow or peripheral blood. These advantages make it a preferred option in many medical scenarios.
3.1. Easier Collection and Storage
Unlike bone marrow, which requires a surgical procedure to extract, cord blood is collected immediately after childbirth without any risk to the mother or baby. The collection process is quick and painless, making it a convenient option for families. Once collected, the cord blood can be processed and stored in a cord blood bank, where it can be cryogenically preserved for years or even decades.
3.2. Lower Risk of Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD)
One of the major risks associated with stem cell transplants is graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), where the transplanted cells attack the recipient’s body. Cord blood stem cells have a lower likelihood of causing GVHD because they are less mature and have not been exposed to environmental antigens. This means that cord blood transplants are generally better tolerated by the recipient, even when the donor is not a perfect match.
3.3. Increased Flexibility in Matching
Cord blood transplants do not require an exact match between donor and recipient, unlike bone marrow transplants, which require a very close match. This flexibility in matching makes cord blood a valuable option for patients who may not be able to find a compatible bone marrow donor. Cord blood can be used in both related and unrelated transplants, offering more opportunities for successful treatment.
4. Public vs. Private Cord Blood Banking
When considering cord blood banking, parents have two main options: public and private banking. Each option has its advantages, and the decision depends on the family’s specific needs and circumstances.
4.1. Public Cord Blood Banking
Public cord blood banks operate similarly to organ donation programs. Parents can choose to donate their baby’s cord blood to a public bank, where it will be available for anyone who needs a transplant. Donating to a public bank is free, and the stored cord blood is available for use by researchers or patients around the world.
The main advantage of public banking is that it increases the overall availability of stem cells for those in need. Many patients who require a stem cell transplant do not have a matching donor in their family, and public cord blood banks provide a crucial resource for these individuals.
4.2. Private Cord Blood Banking
Private cord blood banking allows families to store their baby’s cord blood for their own future use. While private banking can be costly, it gives families peace of mind knowing that they have a genetically matched source of stem cells readily available. This can be particularly beneficial for families with a history of certain genetic conditions or diseases that may require stem cell treatment in the future.
Private cord blood banking is not guaranteed to be needed, but it serves as a form of biological insurance. If the family or a close relative ever needs a stem cell transplant, the stored cord blood can be accessed quickly, providing a potentially lifesaving treatment.
5. The Future of Cord Blood Banking and Research
Cord blood banking is a relatively young field, but ongoing research suggests that its potential applications are expanding. Scientists are continually discovering new ways to use stem cells from cord blood in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
5.1. Emerging Treatments
Researchers are exploring the use of cord blood stem cells in the treatment of conditions like autism, cerebral palsy, and Type 1 diabetes. While these treatments are still in the experimental stages, early results are promising. The regenerative properties of cord blood stem cells could help repair damaged tissue, reduce inflammation, and improve overall function in patients with these conditions.
5.2. Gene Therapy and Personalized Medicine
As the field of gene therapy advances, cord blood stem cells could play a critical role in developing personalized treatments. Researchers are investigating ways to modify stem cells to correct genetic mutations, offering a potential cure for hereditary diseases. The combination of cord blood banking and gene therapy could lead to groundbreaking treatments that target the root cause of many genetic disorders.
5.3. Tissue Regeneration and Organ Repair
Another exciting area of research is the use of cord blood stem cells in tissue regeneration and organ repair. Scientists are studying how stem cells can be used to grow new tissues or even whole organs, which could revolutionize the field of organ transplantation. Cord blood banking could provide the raw material needed for these advanced treatments, offering hope to patients with organ failure or severe injuries.
Cord blood banking offers a unique and valuable opportunity to harness the regenerative power of stem cells for lifesaving treatments. With its proven success in treating blood disorders, cancers, and immune deficiencies, cord blood is already a critical resource in modern medicine. As research continues to unlock new applications for stem cells, the potential benefits of cord blood banking will only grow. Whether choosing public or private banking, parents have the chance to contribute to the future of medicine while securing a potential lifeline for their own families. The lifesaving benefits of cord blood banking are undeniable, making it an important consideration for every new parent.